The ‘.deb’ package is used to install applications on Ubuntu systems. RHEL/CentOS uses RPM as its default package manager. Similarly, we can also install the RPM package on Ubuntu. Debian-based systems, such as RedHat, and Ubuntu-based systems, such as CentOS, Fedora, RHEL, are mostly of the same design. The RedHat operating system displays software packages as .rpm files.
Debian-based systems use .deb files. Therefore, they are designed differently and cannot be installed on platforms other than those you designed them. As if .deb files on CentOS and we can only install RPM files on Debian. Migrating these packages to other systems can be accomplished in several ways. In this article, we will see how to install RPM files on Ubuntu, and we will see how easy it is.
Initially, RPMs were not developed for Debian-based distributions. Ubuntu does not support RPM packages. Installing packaged RPMs on Ubuntu increases the chances of package dependency conflicts. You can install RPM packages in two different ways. Installing .rpm files directly or converting them to .deb files are simple procedures.
Note: RPM packages may not work when installed on Debian-based systems sometimes.
To install RPM packages on
Ubuntu, you need to follow some steps, which are as follows
:
Method 1: Convert RPM file to a
.deb
Installing .rpm files requires converting them to .deb files to make them stable.
First, we need to install the “Alien” software package. This application translates .rpm files into .deb files. To install the Alien software, we first need to add a software repository called “Universe”. Follow the steps below to do this.
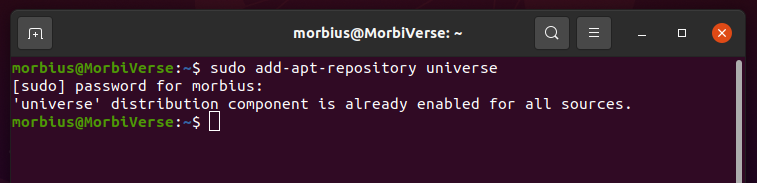
Now, we need to update the system so that we can use the
repository.
After adding the Universe repository, you can install Alien using the following commands:
OR
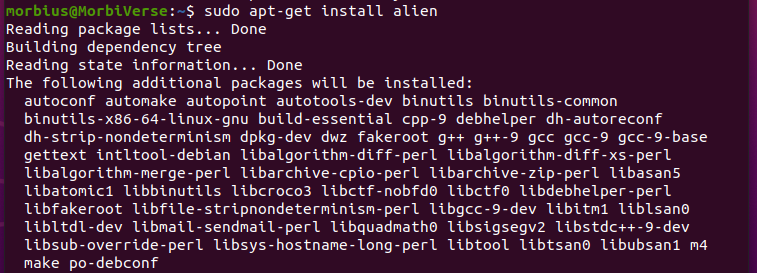
You can use any of the above commands. If you choose to use any of the above commands, you will receive the correct result. For this, type ‘y’ and enter, and the other process continues. If we use the same second command, we rush it with our permission.
For software installation, you need to download a .rpm file. From there, open the location of the file. The RPM file exists. Just copy it and run this command:

As you can see in the image above, we have used Firefox.rpm as a sample page. We have opened Downloads as the current directory in the terminal and then executed the command.
Once finished, the system will display the following message that clearly defines that the RPM package has been successfully converted to a deb package:
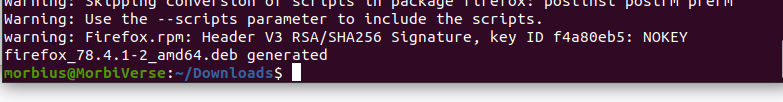
Please note that file conversion may take time. Once converted, you can install the file, usually using dpkg.
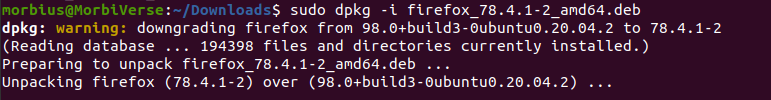
Installing these files is the same as installing a regular .deb package file. After that, you can use the installed software as you normally would.
Method 2: Install RPM Package Directly
on Ubuntu Under this method,
we install the .rpm package on Ubuntu without converting it to a .deb file format beforehand. Under this method,
we also have to use alien software. We can install RPM packages directly through this program. The instructions below are to install an RPM package directly from the terminal window.
This command can cause serious compatibility issues with critical system packages.
Note: Ubuntu does not support all formats, so installing packages in non-native formats can be risky
.
Conclusion
You are less likely to make a mistake if you correctly follow the instructions above. In this article, we have described how we can install the packages. We have explained both methods well here. If you want to know any information related to this article, please tell us by commenting in the comments section.

