When using the file transfer protocol, you may want to know the different elements involved. One element is the FTP port. Successful file transfers can only happen when the correct ports are open.

What are ports?
In FTP terms, ports are communication endpoints. Ports allow the connection and transfer of data to occur between your computer and a server.
To connect to a specific server, you need to know the IP address of that server. While that IP address identifies a particular server, ports are numbers that are used at a lower level to specify which application or service on the server it is trying to communicate with.
IP addresses are unique on the Internet to the server to which they are assigned, but ports are a fixed range of numbers from 0 to 65535 that each server uses
.

How are ports used with file transfer protocols?
When a service that can accept some remote connection (such as an FTP server) starts, it starts “listening” on a specific port. For common services, there is an expected set port that the application should use. The first 1024 ports are reserved for known special services. These services have been assigned a standard port by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
When a file transfer client establishes a
connection to a port on which a file transfer service is listening, it can exchange information. Initially, this is in the form of commands. The commands set the connection details and the operations that you want to perform. The next step is to transfer the requested file data over the same connection or a similarly established connection.
What ports are used for FTP connections?
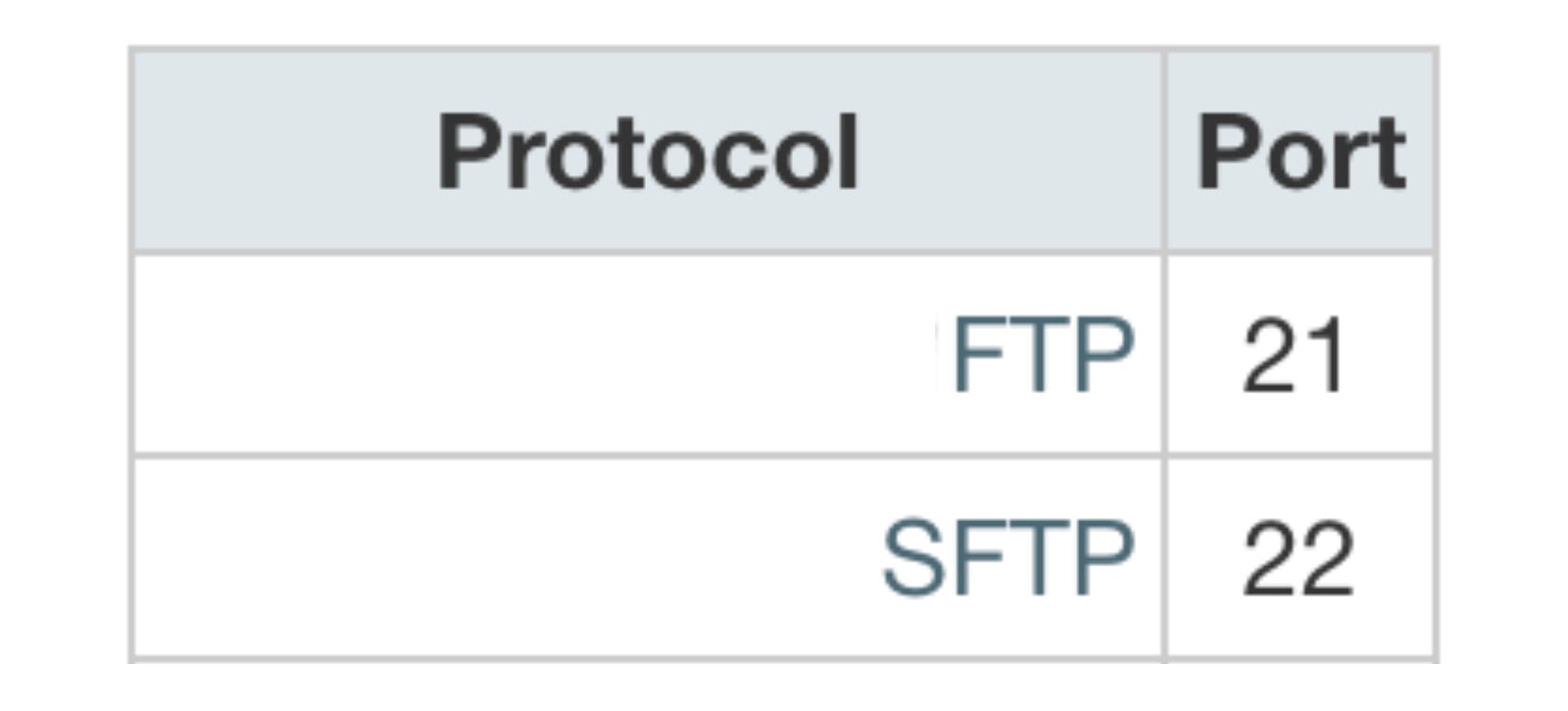
The FTP port
you usually need to know to create a standard unencrypted FTP connection is port 21. For this standard case, this is everything someone using an FTP client needs to know.
Are other FTP ports used for connections?
yes. More ports are used, with differences based on FTP type. Other ports are also used in the case of SFTP, which is a totally different protocol.
FTP has been officially assigned ports 20 and 21. If an “on” connection setting is specifically used, this means that while a client computer makes the connection request and sends commands first on port 21, known as the “control port,” a connection to the server on port 20, the “data port,” also opens automatically to transfer the file data.
If a “passive” FTP connection configuration is used, the client computer also connects to the server on FTP port 21. However, the server responds with a random port number, in a port-free range, to use on the data port for file transfers.
For example, the FTP client will open a control channel on port
21 and a data channel on a random high port in the port range 60000 – 65535
.
Implicit FTPS uses different ports by default, starting with the assigned FTPS port 990 to make the control connection. This initiates an SSL/TLS handshake, then a connection is made to port 989 to transfer the encrypted file data.
SFTP
is
different
SFTP uses a different port. The SFTP port is 22, the same as an SSH connection. In addition, it uses that same port to both control messages and data transfers.
Why is SFTP implemented so differently?
The reason for this is that SFTP is not directly related to FTP. It is a secure transfer protocol over SSH, modeled after the way FTP operates. With SFTP, both connection credentials and transferred data are always encrypted, and you can use SSH keys to authenticate a connection.
Regardless of the protocol you are using, the FTP port or other open ports ensure that you are making the desired connection and that your data is transferred efficiently between the endpoints.

